Non-Ferrous Metal Induction Melting

產品說明
Which Heating Is Used for Melting Non Ferrous Material?
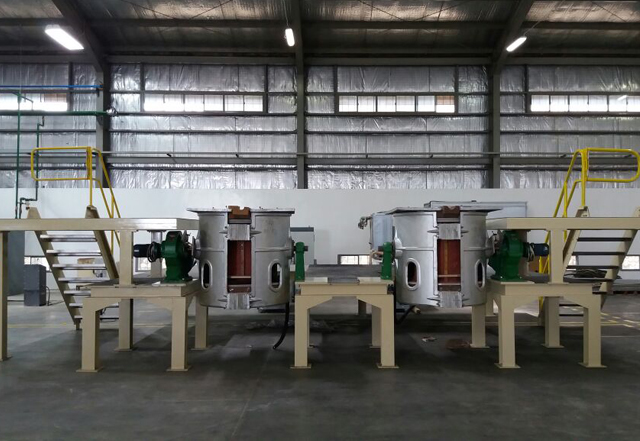
Non-Ferrous Metal Induction Melting
JKZ's non ferrous metal melting furnace can firm the current directly on the graphite crucible or directly on the metal, thereby greatly reducing the heat loss on the furnace itself. With the characteristics of 100% success startup, 100% duty cycle, and power point reach up to 0.98, our industrial induction heating machine china can save 50% electricity than the traditional gas /coal furnaces and save 30-50% electricity than the resistance furnaces. At present, the induction melting furnace used for melting non ferrous metals is widely used in the melting of non-ferrous metals, such as copper, brass, and aluminium, as it holds the irreplaceable advantages of fast heating speed, low cost, environmental protection, low noise, easy maintenance, high efficiency, energy-saving, long use life, small installation space, etc. From a few kilograms to tons of capacity, JKZ can provide you with mature solutions and complete sets of equipment for induction heating non ferrous metals. As a professional induction heater factory, JKZ focuses on small and medium-sized capacity and actually produces 15-500Kgs induction heating smelting furnaces, which can also be customized according to customers' local voltage standard. Aiming to help our customers to purchase economical and suitable equipment for actually use, JKZ china manufacture of induction heating equipment is right here to help you effectively reduce your annual use costs.
Construction of Induction Furnace
There are many different designs of induction furnaces, but they all have some things in common.
The electric coil is placed around or inside the crucible, and the crucible is filled with the metal to be melted. Usually this crucible has two different parts. The lower part stores the melt in its purest form, the metal required by the manufacturer, while the upper part is used to remove slag or contaminants that rise to the surface of the melt.
The crucible can also be equipped with a strong lid to reduce the amount of air entering the molten metal until it is poured out, thereby making the melt more pure
Induction Furnace Working Principle
Induction heating starts with a circle of conductive material (such as copper). Electric current passes through the coil and generates a magnetic field.
The magnetic field can change direction according to the direction of the current. The alternating current passing through the coil generates a magnetic field that changes in the same direction at the same speed as the current.
The induction furnace principle is completely different from that of the cupola. The induction melting furnace uses coil heating elements embedded in the crucible or integrated in the wall of the heating chamber. These convert electrical energy into heat, which is radiated through materials with excellent thermal uniformity.
Restricting the use of combustible fuels in facilities, especially for traditional melting applications, means safer daily operations of personnel and components. The spirally wound induction coil made of refractory heating metal and ceramic can extend the service life and has good compatibility with other control devices. The thermal cycle can be automated, and additional controls can be implemented to reduce the production and emissions of toxic metal vapors in the metal melting furnace.