Metal Tube Rotameter

Apraksts
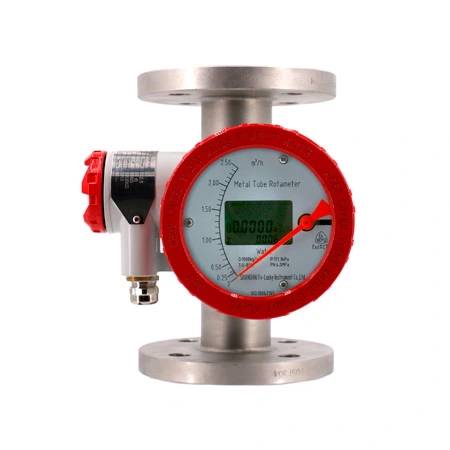
Metal Tube Rotameter
A metal tube rotameter is a variable area flow meter that measures the flow rate of liquids or gases. This metal tube rotameter with transmitter consists of a tapered metal tube and a float. As fluid flows through the tube, the float rises until balanced by its weight, indicating the flow rate on a calibrated scale.
Types of FVLUOKY Metal Tube Rotameter
Flange Type Metal Tube Flowmeter (FFA60-F)
Hoop Type Metal Tube Flowmeter (FFA60-W)
Metal Tube Rotameter Working Principle
The working principle of a metal tube rotameter revolves around the concept of a variable area flow meter, where the flow rate of a fluid (liquid or gas) is measured by allowing it to pass through a tapered tube and observing the position of a float within that tube. Here’s a detailed explanation of its working principle:
1. Tapered Tube:
The metal tube rotameter consists of a vertically oriented, tapered tube made of metal, which is wider at the top and narrower at the bottom. This tube is designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
2. Float:
Inside the tube, there is a freely moving float. This float can be made of different materials (such as stainless steel, glass, or plastic) and comes in various shapes (spherical, cylindrical, or other shapes) depending on the specific application requirements. The density and shape of the float are chosen based on the fluid’s properties and the flow range to be measured.
3. Fluid Flow:
When fluid (either liquid or gas) enters the rotameter from the bottom, it flows upward through the tapered tube. As the fluid flows, it lifts the float. The area between the float and the tube wall increases with the tube’s taper, allowing more fluid to pass around the float.
4. Balancing Force:
The float rises until the upward force exerted by the fluid flow equals the downward gravitational force acting on the float. At this equilibrium position, the area between the float and the tube wall (and thus the flow rate) is constant. The position of the float is directly related to the flow rate of the fluid passing through the meter.
5. Flow Rate Measurement:
The outside of the metal tube is typically marked with a scale that correlates the float’s position to the flow rate. As the float moves up or down with changes in flow, the flow rate can be read directly from this scale.
Key Points:
Variable Area: The principle of operation is based on the variable area created between the float and the tube’s internal wall. As the flow rate changes, this area changes, which moves the float to a new equilibrium position.
Direct Reading: The flow rate can be directly read from the scale on the tube, providing a simple and straightforward measurement.
Versatility: Metal tube rotameters can handle a wide range of fluids, temperatures, and pressures, making them versatile for various industrial applications.
In summary, the metal tube rotameter operates on the principle of balancing the upward fluid force against the weight of the float within a tapered tube, with the float’s position indicating the flow rate.
What Is The Function Of A Rotameter?
The primary function of a rotameter is to measure the flow rate of a fluid (liquid or gas) moving through a closed conduit, such as a pipe or tube. It is a type of variable area flow meter, where the flow rate is determined based on the cross-sectional area that the fluid occupies as it flows through the device. Here are the key functions and features of a rotameter:
1. Flow Rate Measurement:
Direct Measurement: Rotameters provide a direct reading of the flow rate. They are equipped with a scale, calibrated either in volumetric or mass flow units, that indicates the flow rate based on the position of a float within a tapered tube.
Versatility: They can measure the flow rates of both liquids and gases, making them versatile tools in various industrial and laboratory settings.