The difference between off-grid inverter and grid-connected inverter
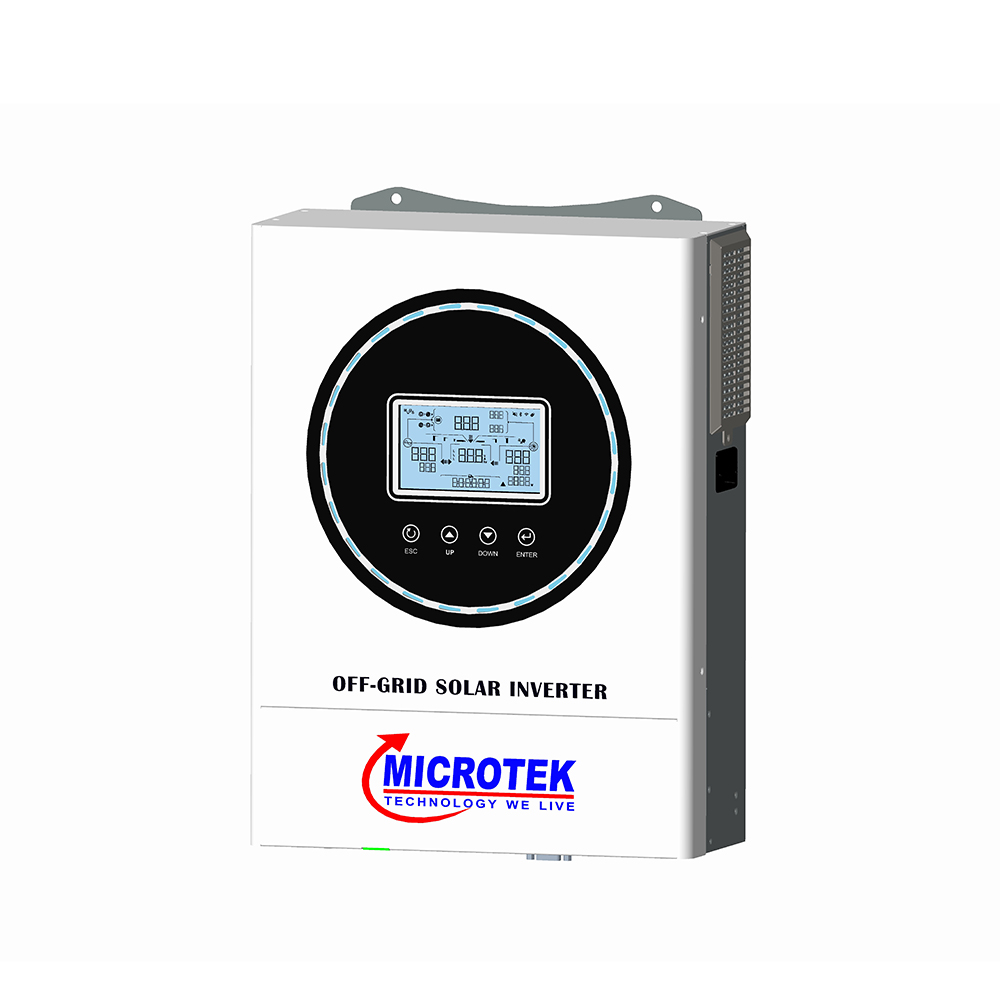

Penerangan produk
Solar energy is becoming more and more important to people, and solar energy systems have become a reality. A family only needs to configure solar panels, solar inverters and batteries to meet household electricity consumption, and any excess power can also be sold to the grid, so that people can be self-sufficient and not let energy go to waste. Solar energy systems have both advantages and disadvantages, we only know both sides of it clearly, in order to make it better for us.
1. Understanding of solar inverters
The use of solar power inverters is to convert the direct current emitted by the solar panels into alternating current, the electricity emitted by the solar panels is all processed through the inverter before it can give output to household appliances, and the use of solar inverters can be divided into: off-grid and grid-connected, so what is the difference between the two?
2. What are the differences between off-grid inverters and grid-connected inverters?
Off-grid inverters usually use a complete system processing solution of modular components, consisting of a number of supervisable components: solar inverter, controller, power generation starter module and system control board. The off-grid inverter is a system that is off the public grid, storing the DC electricity from the solar panels in a battery and then sending it from the battery to the off-grid inverter for inverting out the AC electricity, which can be used directly by the load and can also be returned to the battery for storage. It is suitable for areas without electricity network coverage such as deserts, plateaus and forests.
Grid-connected inverters are usually divided into solar inverters, wind power inverters, grid-connected inverters for electrical equipment and grid-connected inverters for other power generation equipment. Grid-connected inverters are usually used in large power station systems, where a number of parallel photovoltaic strings are connected to the DC input of the same central inverter, usually with three-phase IGBT modules for the more powerful ones and field-effect transistors for the less powerful ones, while a DSP switching controller is used to improve the quality of the electricity produced, making it particularly close to a sinusoidal current. The biggest difference of the grid-connected inverter is that it does not do any battery storage, the DC power formed from the solar panels can be directly switched to AC power through the inverter and sent directly to the public power system, but there is also a corresponding threshold, that is, it needs to meet the relevant regulations and policies of the local power grid, otherwise it is not possible to provide grid connection.